Bacteriophage: category of viruses to infect bacterial cells.
Cloning: identical copy of DNA or an organism.
Cytosine: pyrimidine.
Deoxytibonucleic Acid: molecule of inheritance.
DNA ligase: enzyme that seals new-base pairings.DNA polymerase: enzyme of replication that assembles a new strand of DNA on a parent.
DNA repair: enzyme mediated- process that fixes alterations in a DNA strand by restoring the original sequence.
DNA replication: process by which cell duplicates its DNA molecules before dividing.
Guanine: nitrogen base in one of four nucleotide of DNA and RNA.
Nucelotide: organic compound with deixyrobosue, nitrogen base and phosphate group.
Thymine: one of the nucleotides in DNA.
Anticodon: series of 3 neucleotide of bases in RNA.
Base sequence: sequential order of DNA or RNA.
Base-pair sustitution: amina-acid replacement during protein synthesis.
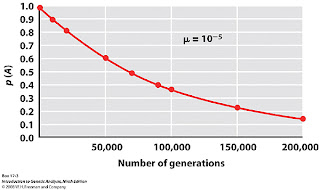
Mutation rate: probability that a spontanous mutation will occur.
Messenger RNA: single stand of ribonucleotides from DNA.
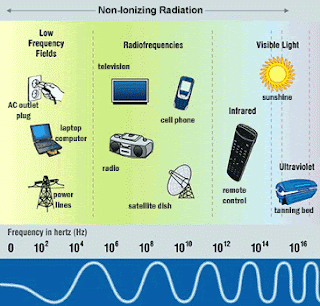
ionizing radiation: high-energy wavelenghts.
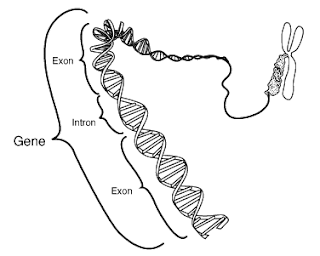
Intron: noncoding portion of pre-mRNA.
Insertion: insertion of one to a few bases into a DNA.
Genetic Code: correspondance between nucleotide sequence of DNA.
Gene Mutation: a small change in the nucleotide sequence of DNA.
Exon: base sequence of a mRNA transcript that will be translated.
Deletion: loss of a segment of a chromosome; loss of one to a few bases on a DNA.
Codon: 64 possibilities base triplets in a mRNA strand.Carcinogen: any substance that can trigger cancer.